Structure-and-Interpretation-of-Computer-Programs-Notes
1 用 Procedures 构建 Abstractions
Lisp 是 LISt Processing 的缩写.
1.1 The Elements of Programming
Lisp 的 prefix notation 可以方便获取 arbitrary number of arguments, 如:
1 | |
另一个好处为便于嵌套组合:
1 | |
pretty-printing:
1 | |
1.1.2 名称和环境
Lisp 中用 define 来命名, 如:
1 | |
environment
为了让 value 和一个 symbols 联系起来, interpreter 需要用一段内存 keeps track of the name-object pairs, 而这段内存就被称为 environment.
1.1.3 Evaluating Combinations
为了计算一个 combinations, interpreter 需要先确定 subexpressions of the combination 的值, 这种计算过程则是 recursive.
下列 process:
1 | |
可以描述为:
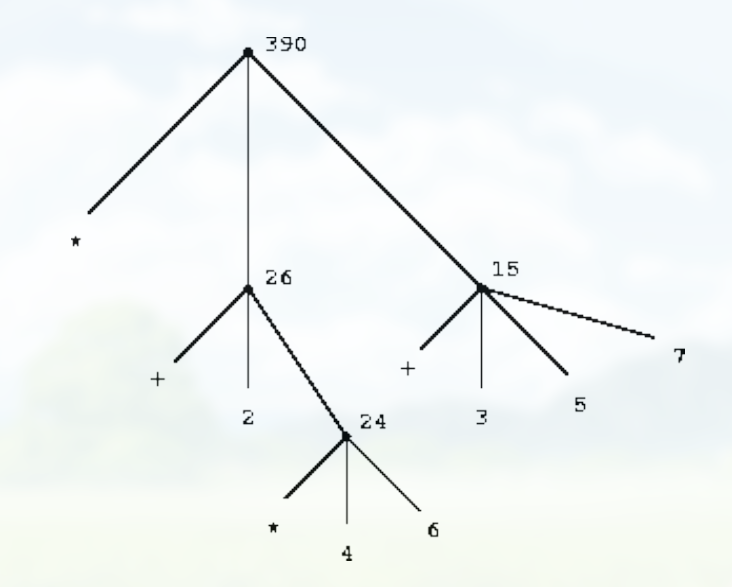
(tree-accumulation 表示)
不产生分支的 nodes 被称为 terminal nodes.
1.1.4 Compound Procedures
procedure definition
形式为:
1 | |
如:
1 | |
normal-order evaluation和applicative-order evaluation
这两个为不同的求值策略 (即表达式中的字表达式什么时候被求值)
normal-order evaluation, 先将表达式完全展开为最简形式, 然后求值, 如:
1 | |
当计算 (example 3 4) 时, 先进行展开:
1.
1 | |
1
(+ (* 3 3) 4)
最后求值:
1 | |
而 applicative-order 先对参数 (子表达式求值), 然后计算出结果, 如求 (example 3 4):
1.
1 | |
1
2(+ 9 4)
13
Lisp 采用的为 applicative-order, 其性能会略高.
1.1.6 条件表达式和 Predicates
Lisp 中的条件语句用 cond (Conditional)
如:
1 | |
类似 (> x 0) 这种就被称为 predicates.
if语句
形式为:
1 | |
如:
1 | |
同样可用 and, or, not
如:
1 | |
1.1.7 用牛顿法求平方根
牛顿法介绍
先简单看下牛顿法的解法.
Newton method 是一种用于寻找方程的数值近似解的迭代算法 (也就是用来解方程), 其基本思想是从一个初始猜测的解开始,通过不断改进的迭代过程,逐渐接近方程的真实解。具体步骤如下:
选择一个初始猜测值(通常是方程的一个近似解)作为起点。
在当前猜测值处,计算方程的函数值和导数值。函数值表示方程与当前猜测值的差距,导数值表示方程的斜率。
使用当前猜测值和函数值、导数值的信息,通过牛顿迭代公式进行迭代计算,得到下一个猜测值。
重复步骤2和步骤3,直到达到预设的停止条件(例如,达到预设的精度要求或迭代次数)
如:
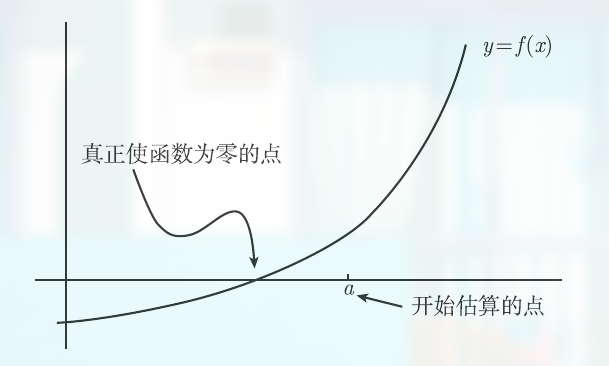
接着通过 f 在 x=a 处的线性化来改善估算:
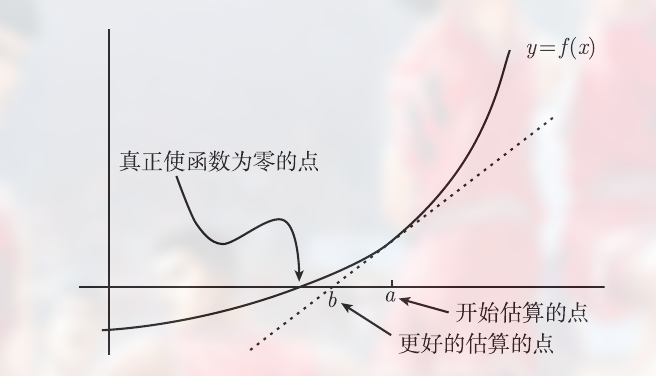
此时 b 的值为:
$$
\displaylines
{
\begin{aligned}
L(x) = f(a) + f’(a)(x-a)
\end{aligned}
}
$$
在 x 轴的截距.
可以解出:
$$
\displaylines
{
\begin{aligned}
x = a - \frac{f(a)}{f’(a)}
\end{aligned}
}
$$
因此得到的牛顿法的公式为:
$$
\displaylines
{
\begin{aligned}
b = a - \frac{f(a)}{f’(a)}
\end{aligned}
}
$$
之后就是不断迭代, 求出最优解.
在有些情况下牛顿法会不起作用:
f'(a)的值接近于 0f(x) = 0有不止一个解- 用牛顿法时, 近似越来越糟糕或循环.
Lisp 实现
1 | |
1.2 Procedures and the Processes They Generate
1.2.1 Linear Recursion and Iteration
以 deferred operation 进行收缩的过程即 recursive process, 编译器需要记录以后会执行的操作.
Iteration 的状态可以用一系列 iterative evariables 表示. Iteration 操作维护一组变量. 其关键特点是, 在递归调用之前不会有其他操作或表达式需要执行. 这使得编译器或解释器可以对尾递归进行优化, 以避免创建额外的函数调用栈帧 (函数的执行环境).相反, 它可以重用当前函数的调用栈帧, 从而节省内存空间, 并使递归函数的执行效率更高.