简介 CORS, Cross-Origin Response Sharing, 跨域资源共享. 是一个 Web 安全机制, 用于管理跨域 HTTP 请求.
其通常指浏览器中运行的前端拥有与后端通信的 JavaScript 代码, 而后端处于与前端不同的 “源” 的情况.
源是协议 (http,https), 域 (myapp.com, localhost, localhost.tiangolo.com) 以及端口 (80, 443, 8080) 的组合.
因此, 这些都是不同的源:
出于安全原因, 大多数现代浏览器都会阻止这种跨域请求, 除非目标服务器明确允许这种跨域访问.
除非设置一个 “允许的源” 的列表.
比如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package mainimport ("encoding/json" "net/http" type ApiResponse struct {string `json:"message"` func main () "/" , dataHandler)":8080" , nil )func dataHandler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) "Hello from the Golang API!" }
React 部署在 http://localhost:3000, 前端 JS 为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import { useState, useEffect } from 'react' ;export default function Test (const [data, setData] = useState (null );async function fetchData (try {const response = await fetch ('http://localhost:8080/' );const data = await response.json ();setData (data)catch (error) {console .error ('Error: ' , error);useEffect (() => {fetchData ();if (!data) {return <div > Loading...</div > return (<h1 > {data.message}</h1 >
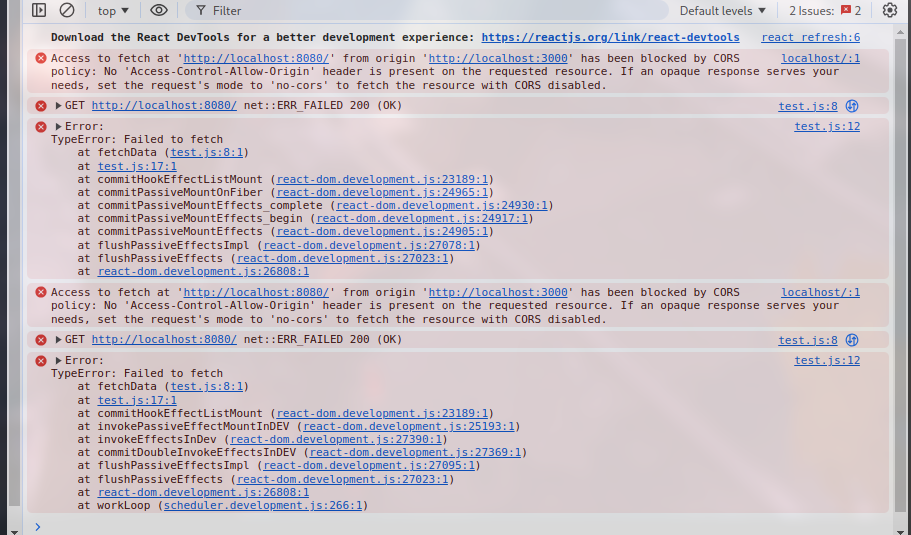
此时会出现 CORS error:
可以通过配置 CORS 策略来解决.
CORS 策略的工作原理
当浏览器检测到一个跨域请求时, 它会先向服务器发送一个 “预检” 请求(OPTIONS 请求), 询问目标服务器是否允许该跨域请求
如果服务器返回允许跨域访问的响应头, 浏览器就会发送实际的请求. 否则, 浏览器会阻止请求
而决定是否允许的, 则是 CORS 策略. 通常需要包括允许的源, 方法和头部.
导入 1 2 3 import ("github.com/rs/cors"
创建 CORS 处理程序 需要传入 cors.Option 类型数据给 cors.New() 来创建:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 c := cors.New(cors.Options{string {"http://localhost:3000" },string {"GET" , "POST" , "PUT" , "DELETE" , "OPTIONS" },string {"Content-Type" , "Authorization" },string {"Link" },true ,300 ,
示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package mainimport ("encoding/json" "net/http" "github.com/rs/cors" type ApiResponse struct {string `json:"message"` func main () string {"http://localhost:3000" },string {"GET" , "POST" , "PUT" , "DELETE" , "OPTIONS" },string {"Content-Type" , "Authorization" },string {"Link" },true ,300 , "/" , dataHandler)":8080" , handler)func dataHandler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) "Hello from the Golang API!" }
http.DefaultServeMux 也是一个 http.Handler 类型, 负责将传入的 HTTP 请求路由到正确的处理程序(handler)上c.Handler() 返回一个 http.Handler 类型. 其将 http.DefaultServeMux 包装成一个新的 HTTP 处理器. 这个新的处理器会在调用时, 先应用 CORS 规则, 然后再将请求路由到 http.DefaultServeMux 上注册的处理程序