FastAPI Github 仓库
FastAPI 官方文档
介绍 FastAPI 是一个用于构建 Web API 的 Python 框架.
安装 1 pip install "fastapi[all]"
(这里其实包括 uvicorn 的安装了)
另外要安装一个 ASGI (Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface, 负责在网络请求和 Python 应用程序之间进行通信) 服务器, 如 Uvicorn:
1 pip install "uvicorn[standard]"
示例 创建 main.py 并写入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/" async def read_root ():return {"Hello" : "World" }
运行:
1 uvicorn main:app --reload
main:app, 前者指运行 main.py 文件, 后者指定文件中创建的 FastAPI 实例名称--reload, 指启用自动重载,当代码更改时,服务器会自动重启
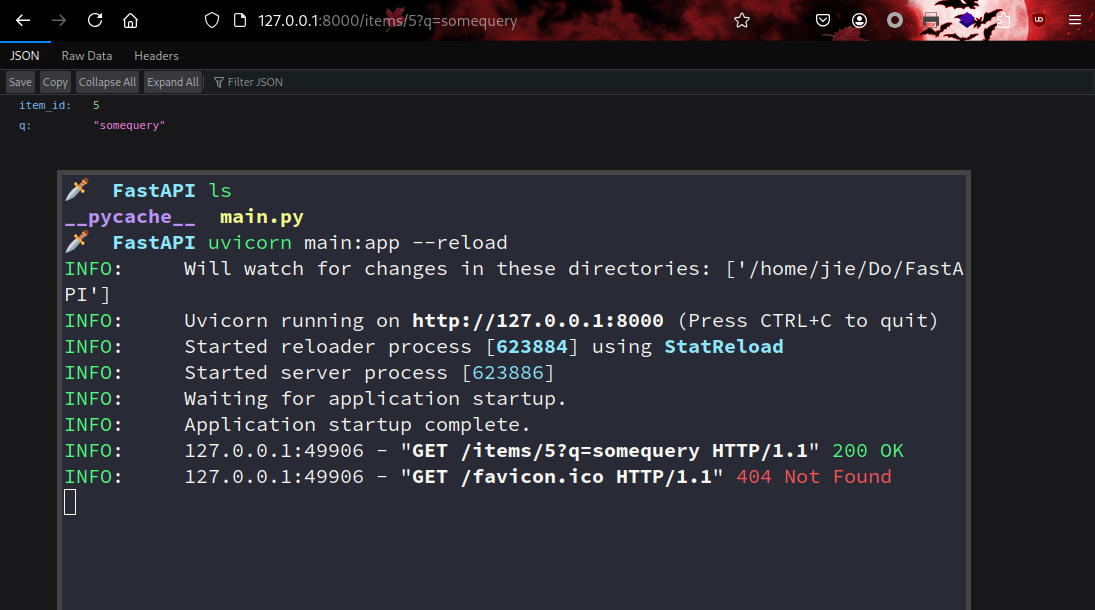
用浏览器访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery 来测试:
调试 可以访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs 或 http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc 来调试 API.
语法 路径参数 可以理解为变量插值 (实际上是用来捕获), 可以使用 {var} 的语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_item (item_id ):return {"item_id" : item_id}
路径顺序 注意路径的匹配是按照编写顺序的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/users/me" async def read_user_me ():return {"user_id" : "the current user" }@app.get("/users/{user_id}" async def read_user (user_id: str ):return {"user_id" : user_id}
若反过来行为就会不同. (反过来的情况, 比如访问 /users/me 这里的 me 会被 {user_id} 捕获)
预定义值 需要借助 Enum 类来实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from enum import Enumfrom fastapi import FastAPIclass ModelName (str , Enum):"alexnet" "resnet" "lenet" @app.get("/models/{model_name}" async def get_model (model_name: ModelName ):if model_name is ModelName.alexnet:return {"model_name" : model_name, "message" : "Deep Learning FTW!" }if model_name.value == "lenet" :return {"model_name" : model_name, "message" : "LeCNN all the images" }return {"model_name" : model_name, "message" : "Have some residuals" }
通过继承 str 类, 可以把该枚举值定义为 “字符串”.
路径参数 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/files/{file_path:path}" async def read_file (file_path: str ):return {"file_path" : file_path}
{file_path:path}, 这里的 file_path 就是路径参数, :path 是修饰, 其表明 file_path 捕获任意长度的路径, 如 /files/a/b/c, 那么 file_path 的值为 a/b/c
查询参数 即:
1 http:// 127.0 .0.1 :8000 /items/ ?skip=0 &limit=10
这里的 skip 和 limit 就是查询参数.
体现在 FastAPI 中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from fastapi import FastAPI"item_name" : "Foo" }, {"item_name" : "Bar" }, {"item_name" : "Baz" }]@app.get("/items/" async def read_item (skip: int = 0 , limit: int = 10 ):return fake_items_db[skip : skip + limit]
这里同时给 skip 和 limit 设置了默认值.
类型注解和可选参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_item (item_id: str , q: str | None = None ):if q:return {"item_id" : item_id, "q" : q}return {"item_id" : item_id}
这里的 str | None 就是类型注解, 表明其可以是 str 类型, 也可以是 None 类型, 而当用户没有提供 q 变量时, 其就为 None 类型且默认值为 None.
必选参数 不给参数指定默认值, 那它就为必选参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_user_item (item_id: str , needy: str ):"item_id" : item_id, "needy" : needy}return item
这里的 needy 就是必选参数, 若访问:
1 http:// 127.0 .0.1 :8000 /items/ foo-item
则会返回错误响应. 正常应为:
1 http:// 127.0 .0.1 :8000 /items/ foo-item?needy=sooooneedy
请求体 借助 Pydantic 库 (一个用于数据验证和文档化的 python 库), 一般用其中的 BaseModel 类.
可以转换为字典, JSON 序列化等:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item (BaseModel ):str str | None = None float float | None = None @app.post("/items/" async def create_item (item: Item ):return item
这里实际上是返回:
1 2 3 4 5 6 { "name" : "Foo" , "description" : "An optional description" , "price" : 45.2 , "tax" : 3.5 }
即一个 Python 字典 (也是 JSON 对象).
这里的 item 就是请求体.
若要以字典访问 BaseModel 类实例, 需使用 dict() 方法如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item (BaseModel ):str str | None = None float float | None = None @app.post("/items/" async def create_item (item: Item ):dict ()if item.tax:"price_with_tax" : price_with_tax})return item_dict
给查询参数添加约束 比如, 对于一个查询参数而言, 不能超过 50 个字符的长度, 可以写为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from typing import Union from fastapi import FastAPI, Query@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (q: Union [str , None ] = Query(default=None , max_length=50 ) ):"items" : [{"item_id" : "Foo" }, {"item_id" : "Bar" }]}if q:"q" : q})return results
设置查询参数的默认值为 Query.
Query 函数的第一个参数用于设置默认值 (比如原来的 None 就写在这里了), 而余下参数用于设置约束.
比如:
1 q: Union [str , None ] = Query(default=None )
等价于:
添加更多约束的示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from typing import Union from fastapi import FastAPI, Query@app.get("/items/" async def read_items ( q: Union [str , None ] = Query( default=None , min_length=3 , max_length=50 , pattern="^fixedquery$" ),"items" : [{"item_id" : "Foo" }, {"item_id" : "Bar" }]}if q:"q" : q})return results
用 Query 接收一组值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from typing import List , Union from fastapi import FastAPI, Query@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (q: Union [List [str ], None ] = Query(default=None ) ):"q" : q}return query_items
添加元数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from typing import Union from fastapi import FastAPI, Query@app.get("/items/" async def read_items ( q: Union [str , None ] = Query( default=None , alias="item-query" , title="Query string" , description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match" , min_length=3 , max_length=50 , pattern="^fixedquery$" , deprecated=True , ),"items" : [{"item_id" : "Foo" }, {"item_id" : "Bar" }]}if q:"q" : q})return result
这里的;
alias
title
description
deprecated
就是元数据
给路径参数添加约束和元数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Query@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_items ( item_id: Annotated[int , Path(title="The ID of the item to get" )], q: Annotated[str | None , Query(alias="item-query" )] = None , "item_id" : item_id}if q:"q" : q})return results
数值校验示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Query@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_items ( *, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get" , ge=0 , le=1000 ), q: str , size: float = Query(gt=0 , lt=10.5 ), "item_id" : item_id}if q:"q" : q})return results
有多个参数的请求体 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item (BaseModel ):str str | None = None float float | None = None class User (BaseModel ):str str | None = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}" async def update_item (item_id: int , item: Item, user: User ):"item_id" : item_id, "item" : item, "user" : user}return results
其期望的请求体为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 { "item" : { "name" : "Foo" , "description" : "The pretender" , "price" : 42.0 , "tax" : 3.2 } , "user" : { "username" : "dave" , "full_name" : "Dave Grohl" } }
向请求体添加一个键 也就是期望请求的 JSON 中多一个键值对, 借助 fastapi 提供的 Body():
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item (BaseModel ):str str | None = None float float | None = None class User (BaseModel ):str str | None = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}" async def update_item ( item_id: int , item: Item, user: User, importance: Annotated[int , Body( "item_id" : item_id, "item" : item, "user" : user, "importance" : importance}return results
其期望:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 { "item" : { "name" : "Foo" , "description" : "The pretender" , "price" : 42.0 , "tax" : 3.2 } , "user" : { "username" : "dave" , "full_name" : "Dave Grohl" } , "importance" : 5 }
也可以给 Body() 传递约束和元数据.
模型内部进行约束和元数据设置 使用 Pydantic 中的 Field:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldclass Item (BaseModel ):str str | None = Field(None , title="The description of the item" , max_length=300 float = Field(gt=0 , description="The price must be greater than zero" )float | None = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}" async def update_item (item_id: int , item: Annotated[Item, Body(embed=True )] ):"item_id" : item_id, "item" : item}return results
添加额外文档信息 给 Field, Body, Path, Query 添加 example 参数即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldclass Item (BaseModel ):str = Field(examples=["Foo" ])str | None = Field(default=None , examples=["A very nice Item" ])float = Field(examples=[35.4 ])float | None = Field(default=None , examples=[3.2 ])@app.put("/items/{item_id}" async def update_item (item_id: int , item: Item ):"item_id" : item_id, "item" : item}return results
声明 Cookie 参数 给查询参数添加 Cookie() 的类型注释就行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (ads_id: Annotated[str | None , Cookie(None ):return {"ads_id" : ads_id}
给查询参数添加 Header() 的类型注释就行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Header@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (user_agent: Annotated[str | None , Header(None ):return {"User-Agent" : user_agent}
处理响应类型 即 response_model, 是 get, post 等修饰器方法的参数.
用来将输出数据转换为指定类型以及数据校验等.
如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from typing import Any from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrclass UserIn (BaseModel ):str str str | None = None class UserOut (BaseModel ):str str | None = None @app.post("/user/" , response_model=UserOut async def create_user (user: UserIn ) -> Any :return user
使用多个模型 主要借助继承以及模型间的转换:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrclass UserBase (BaseModel ):str str | None = None class UserIn (UserBase ):str class UserOut (UserBase ):pass class UserInDB (UserBase ):str def fake_password_hasher (raw_password: str ):return "supersecret" + raw_passworddef fake_save_user (user_in: UserIn ):dict (), hashed_password=hashed_password)print ("User saved! ..not really" )return user_in_db@app.post("/user/" , response_model=UserOut async def create_user (user_in: UserIn ):return user_saved
借助 Union 使用多个模型中的某个:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 from typing import Union from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass BaseItem (BaseModel ):str type : str class CarItem (BaseItem ):type : str = "car" class PlaneItem (BaseItem ):type : str = "plane" int "item1" : {"description" : "All my friends drive a low rider" , "type" : "car" },"item2" : {"description" : "Music is my aeroplane, it's my aeroplane" ,"type" : "plane" ,"size" : 5 ,@app.get("/items/{item_id}" , response_model=Union [PlaneItem, CarItem] async def read_item (item_id: str ):return items[item_id]
指定响应状态码 使用 status_code 参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from fastapi import FastAPI@app.post("/items/" , status_code=201 async def create_item (name: str ):return {"name" : name}
接收表单数据 使用 Form() 函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from fastapi import FastAPI, Form@app.post("/login/" async def login (username: str = Form(str = Form( ):return {"username" : username}
接收文件 需要先安装 python-multipart:
1 pip install python-multipart
使用 File() 函数或 UploadFile 类.
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFilefrom fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse@app.post("/files/" async def create_files ( files: list [bytes ] = File(description="Multiple files as bytes" ), return {"file_sizes" : [len (file) for file in files]}@app.post("/uploadfiles/" async def create_upload_files ( files: list [UploadFile] = File(description="Multiple files as UploadFile" ), return {"filenames" : [file.filename for file in files]}@app.get("/" async def main ():""" <body> <form action="/files/" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post"> <input name="files" type="file" multiple> <input type="submit"> </form> <form action="/uploadfiles/" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post"> <input name="files" type="file" multiple> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> """ return HTMLResponse(content=content)
接收 PDF 文件的完整示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFilefrom fastapi.responses import HTMLResponseimport shutilimport osfrom pathlib import Path"./uploads" True )@app.get("/" , response_class=HTMLResponse async def main ():return """ <html> <head> <title>Upload PDF</title> </head> <body> <h1>Upload a PDF file</h1> <form action="/uploadfile/" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="file" accept=".pdf" required> <button type="submit">Upload</button> </form> </body> </html> """ @app.post("/uploadfile/" async def upload_file (file: UploadFile = File(... ) ):if file.filename != None :if not Path(file.filename).suffix == '.pdf' :return {"error" : "Only PDF files are allowed." }with open (file_path, "wb" ) as buffer:return {"filename" : file.filename, "filepath" : file_path}else :raise Exception("File name is None" )
错误处理 使用 HTTPException 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException"foo" : "The Foo Wrestlers" }@app.get("/items/{item_id}" async def read_item (item_id: str ):if item_id not in items:raise HTTPException(status_code=404 , detail="Item not found" )return {"item" : items[item_id]}
注意这里用 raise 来触发 HTTPException.
定义异常处理器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 from fastapi import FastAPI, Requestfrom fastapi.responses import JSONResponseclass UnicornException (Exception ):def __init__ (self, name: str ):@app.exception_handler(UnicornException ) async def unicorn_exception_handler (request: Request, exc: UnicornException ):return JSONResponse(418 ,"message" : f"Oops! {exc.name} did something. There goes a rainbow..." },@app.get("/unicorns/{name}" async def read_unicorn (name: str ):if name == "yolo" :raise UnicornException(name=name)return {"unicorn_name" : name}
路径修饰 给要访问的路径添加一些数据, 如 summary, description, response_description 参数, 以及函数多行注释:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from typing import Set , Union from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item (BaseModel ):str Union [str , None ] = None float Union [float , None ] = None Set [str ] = set ()@app.post( "/items/" , response_model=Item, summary="Create an item" , response_description="The created item" , async def create_item (item: Item ):""" Create an item with all the information: - **name**: each item must have a name - **description**: a long description - **price**: required - **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this - **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item """ return item
依赖项 就是提前运行一个函数, 返回一些依赖数据.
函数作为依赖项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from typing import Union from fastapi import Depends, FastAPIasync def common_parameters ( q: Union [str , None ] = None , skip: int = 0 , limit: int = 100 return {"q" : q, "skip" : skip, "limit" : limit}@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters ) ):return commons@app.get("/users/" async def read_users (commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters ) ):return commons
注意这里的 Dependsh 指接受一个参数, 且参数需要是一个可调用对象.
类作为依赖项 类也是可调用对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI"item_name" : "Foo" }, {"item_name" : "Bar" }, {"item_name" : "Baz" }]class CommonQueryParams :def __init__ (self, q: str | None = None , skip: int = 0 , limit: int = 100 ):@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends(CommonQueryParams ) ):if commons.q:"q" : commons.q})"items" : items})return response
可以把:
1 2 3 ...async def read_items (commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends(CommonQueryParams ) ):
简写为:
1 2 3 ...async def read_items (commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends( ):
不使用依赖项的返回值 当只需要执行依赖项而不需要其返回值时, 在 “路径操作修饰器” 中用 dependencies 指定一个 list:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Header, HTTPExceptionasync def verify_token (x_token: str = Header( ):if x_token != "fake-super-secret-token" :raise HTTPException(status_code=400 , detail="X-Token header invalid" )async def verify_key (x_key: str = Header( ):if x_key != "fake-super-secret-key" :raise HTTPException(status_code=400 , detail="X-Key header invalid" )return x_key@app.get("/items/" , dependencies=[Depends(verify_token ), Depends(verify_key )] async def read_items ():return [{"item" : "Foo" }, {"item" : "Bar" }]
定义全局依赖项 比如让每一个路径操作修饰器都会触发几个依赖项函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Header, HTTPExceptionasync def verify_token (x_token: str = Header( ):if x_token != "fake-super-secret-token" :raise HTTPException(status_code=400 , detail="X-Token header invalid" )async def verify_key (x_key: str = Header( ):if x_key != "fake-super-secret-key" :raise HTTPException(status_code=400 , detail="X-Key header invalid" )return x_key@app.get("/items/" async def read_items ():return [{"item" : "Portal Gun" }, {"item" : "Plumbus" }]@app.get("/users/" async def read_users ():return [{"username" : "Rick" }, {"username" : "Morty" }]
安全验证 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from fastapi import Depends, FastAPIfrom fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer"token" )@app.get("/items/" async def read_items (token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme ) ):return {"token" : token}
这里的 tokenUrl 指定的是相对访问路径, 如这里在 /items/ 下, 因此该为 /items/token.
表单会将 username 和 password 发送到该路径, API 在验证之后会响应一个令牌, 之后若要验证身份, 只需要发送值为 Bearer+令牌 的 Authorization 请求头.
中间件 即一个可以在 “请求” 被 “路径操作” 处理前运行, 或在 “响应” 返回前运行的函数.
需要使用 @app.middleware("http) 修饰器来创建. 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import timefrom fastapi import FastAPI, Request@app.middleware("http" async def add_process_time_header (request: Request, call_next ):await call_next(request)"X-Process-Time" ] = str (process_time)return response
call_next 会把 request 传递给相应的路径操作函数处理以获取 response
CORS 在 FastAPI 中用 CORSMiddleware 来配置, 一般步骤为:
创建一个允许的源列表
将其作为中间件添加到 FastAPI 应用中
创建列表示例为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware"http://localhost.tiangolo.com" ,"https://localhost.tiangolo.com" ,"http://localhost" ,"http://localhost:8080" ,True ,"*" ],"*" ],@app.get("/" async def main ():return {"message" : "Hello World" }
SQL 数据库 ORMs ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) 是一种编程技术, 它允许你使用面向对象的方式来操作数据库, 而不需要直接编写 SQL 语句.
ORM 的核心思想是将数据库表映射为对象(称为模型或实体), 每个表对应一个类, 每个行对应一个对象实例, 每一列对于一个类成员. 开发者可以使用面向对象的方式来创建, 读取, 更新和删除数据, 而不需要直接与数据库进行交互.
在 Python 中一般使用 SQLAlchemy 包的 ORM 实现. 安装为:
后台任务 指返回响应之后执行的任务.
使用 BackgroundTasks 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from fastapi import BackgroundTasks, FastAPIdef write_notification (email: str , message="" ):with open ("log.txt" , mode="w" ) as email_file:f"notification for {email} : {message} " @app.post("/send-notification/{email}" async def send_notification (email: str , background_tasks: BackgroundTasks ):"some notification" )return {"message" : "Notification sent in the background" }
步骤为:
设置元数据 给 FastAPI 创建的应用实例添加元数据, 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 from fastapi import FastAPI""" ChimichangApp API helps you do awesome stuff. 🚀 ## Items You can **read items**. ## Users You will be able to: * **Create users** (_not implemented_). * **Read users** (_not implemented_). """ "ChimichangApp" ,"Deadpool's favorite app. Nuff said." ,"0.0.1" ,"http://example.com/terms/" ,"name" : "Deadpoolio the Amazing" ,"url" : "http://x-force.example.com/contact/" ,"email" : "dp@x-force.example.com" ,"name" : "Apache 2.0" ,"url" : "https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html" ,@app.get("/items/" async def read_items ():return [{"name" : "Katana" }]
静态文件 即提供静态文件的响应, 像文件服务器, 使用 StaticFiles 如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles"/static" , StaticFiles(directory="static" ), name="static" )
把 StaticFiles() 指定的目录挂载到 /static 这个 url 下.
测试 主要借助 pytest 运行测试文件. 安装为:
使用 TestClient 测试, 需要先安装 httpx:
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from fastapi import FastAPIfrom fastapi.testclient import TestClient@app.get("/" async def read_main ():return {"msg" : "Hello World" }def test_read_main ():"/" )assert response.status_code == 200 assert response.json() == {"msg" : "Hello World" }
将 FastAPI 应用传递给 TestClient() 以创建一个 TestClient 对象.
之后直接运行:
即可.
分离测试 若文件结构为:
1 2 3 4 5 ..py main .py
则测试文件 test_main.py 文件内容为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from fastapi.testclient import TestClientfrom .main import appdef test_read_main ():"/" )assert response.status_code == 200 assert response.json() == {"msg" : "Hello World" }
命令行工具 在用:
安装 FastAPI 库之后, 会提供 fastapi 命令, 可用于部署, 运行和管理 FastAPI 项目.
开发模式运行 此时当你更改代码时, 它会自动重新加载服务器.
此时默认监听 127.0.0.1.
生产模式运行 此时不会自动重载, 且监听 0.0.0.0.